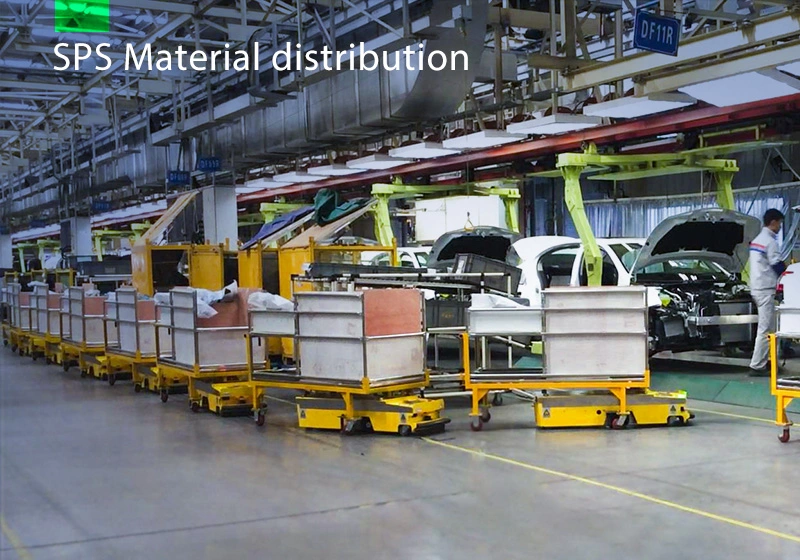
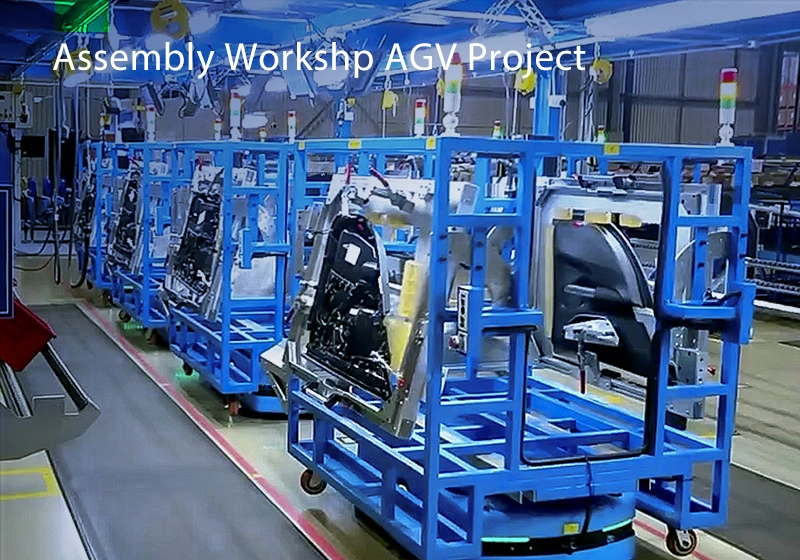
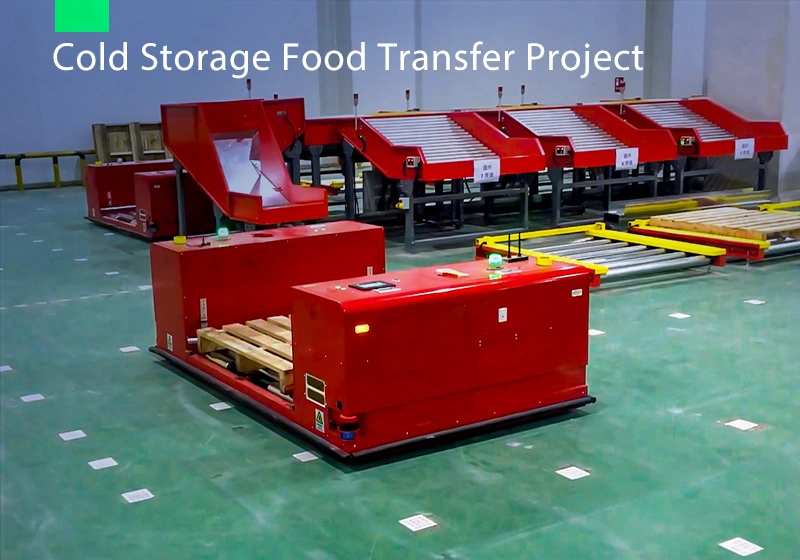
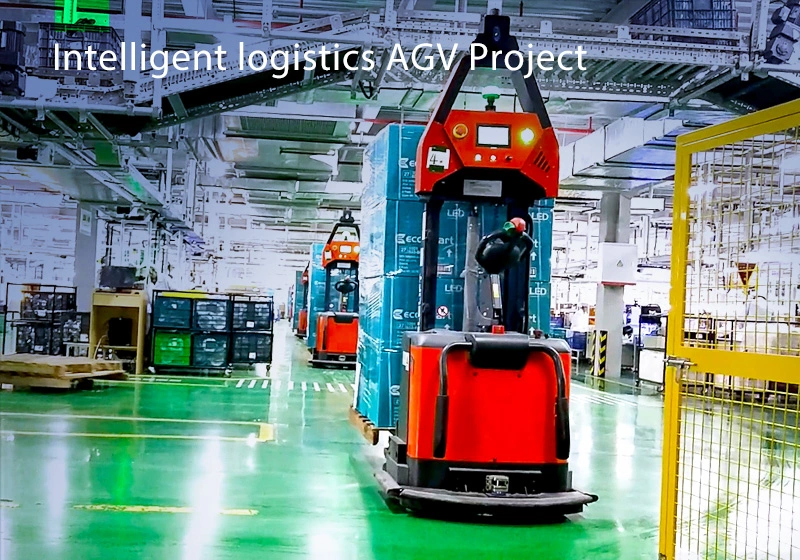
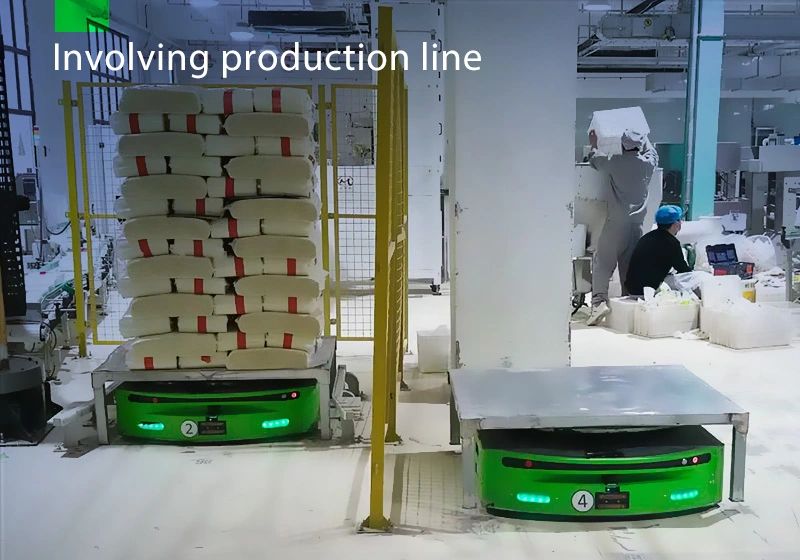
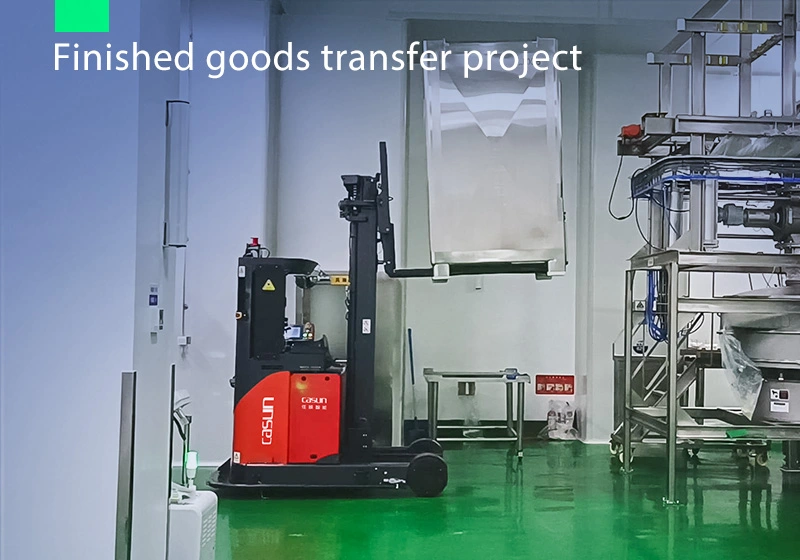
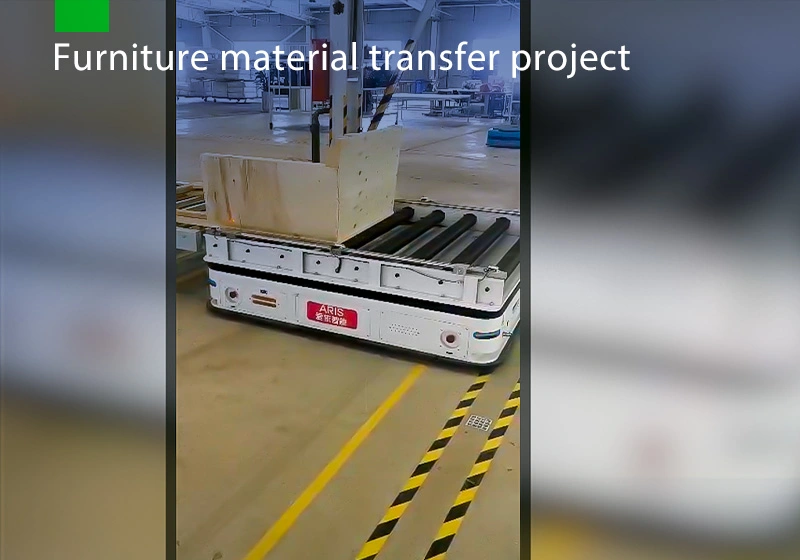
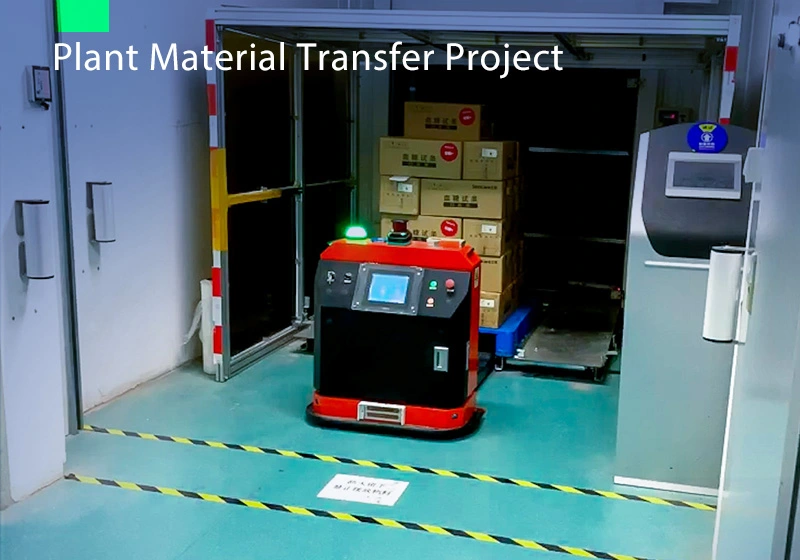
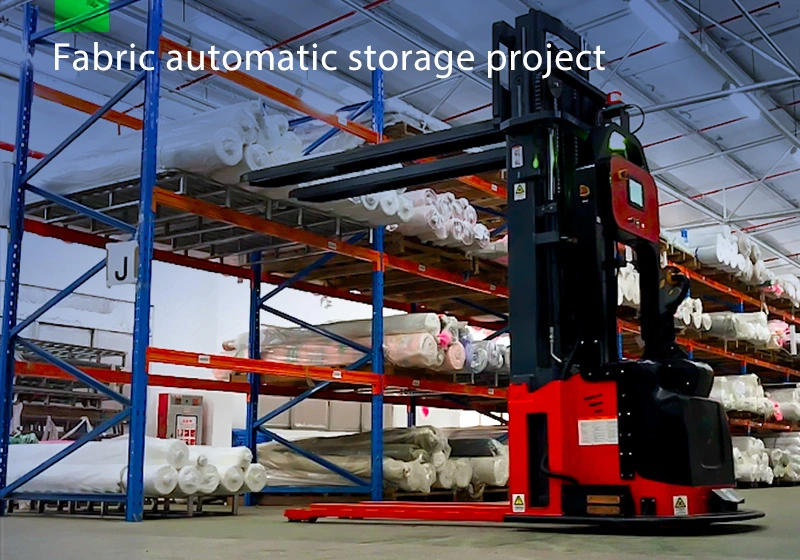
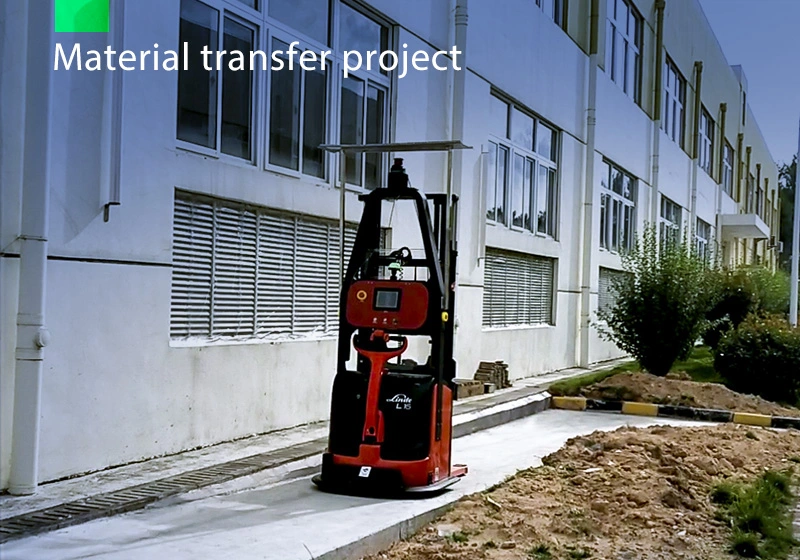
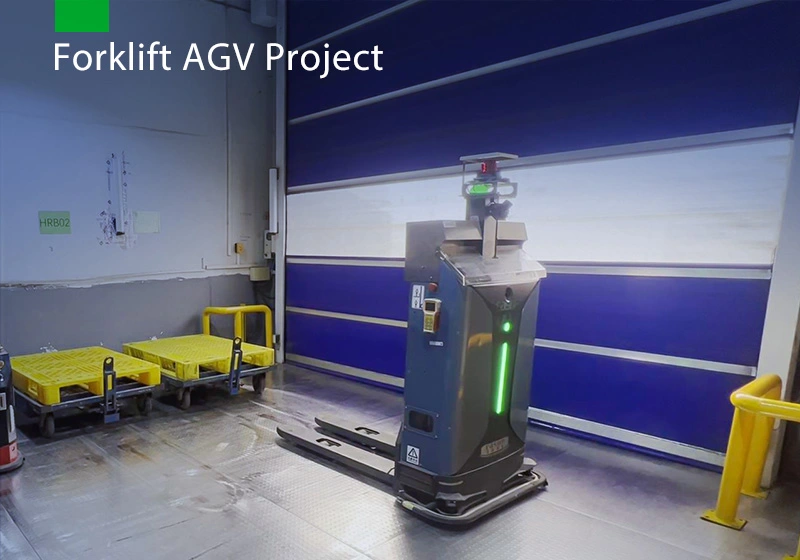
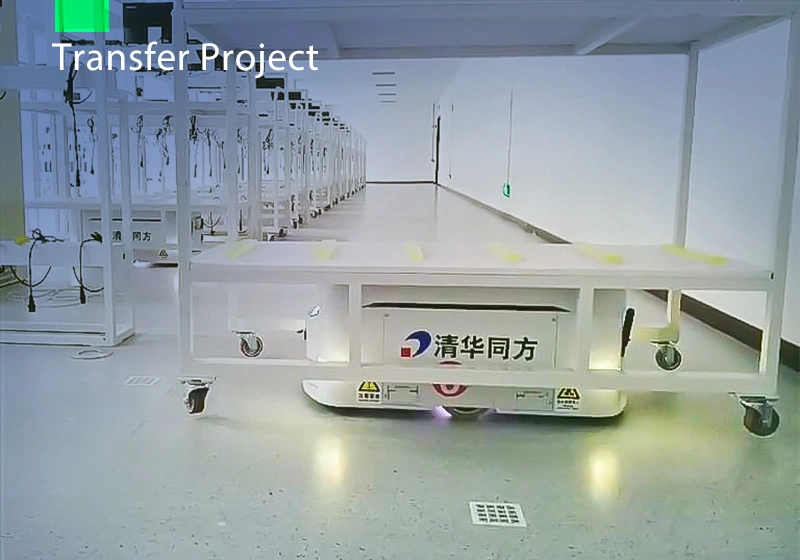
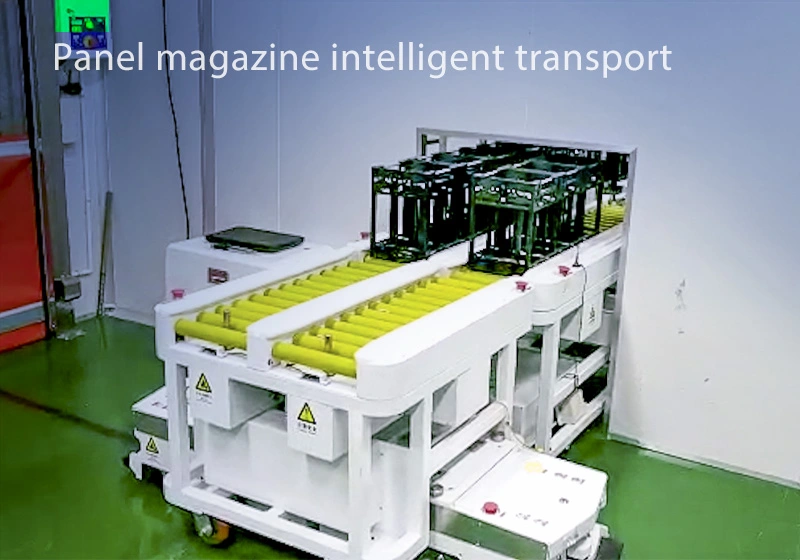
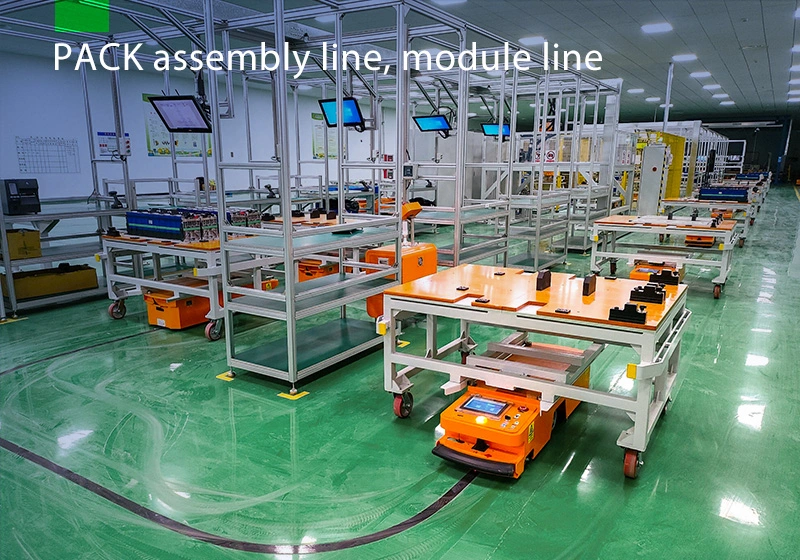
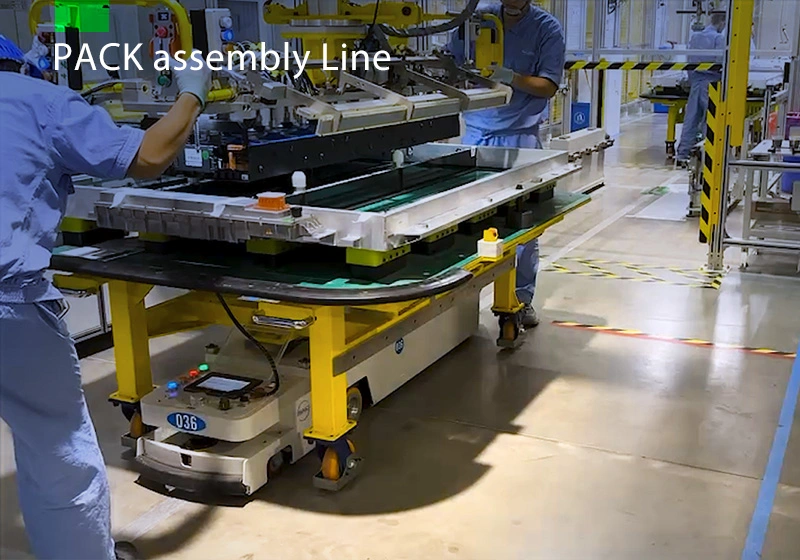
Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
 Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
Charging mode | Collision charging |
Model | CCS-31 |
Dimension | L490*W385*H355(mm) |
| Voltage | Power |
| 24V | 1500W-5000W |
| 48V | 1500W-5000W |
AGV is installed with a charging contact plate. The electrical power circuit between the contact plate and battery is controlled by the contractor. When AGV is not undercharging state, the circuit between the contact plate and battery is the off-state. The charging station is connected with the contact plate through a contractor. The charging station is installed with the current collector, when the electrical circuit is closed, the charging station will test the power voltage. Only when voltage is detected, the charging station will start to charge, thus avoiding a short circuit. When AGV is under an automatically charging state, it goes to a defined charging area. With a precise positioning method, the contact plate on AGV can connect with the current collector on the ground. Then through connection signal exchange, the AGV charging contactor is on, and the charging station starts to charge after the input voltage is detected.
The onboard controller will read the battery percentage, which will be displayed on the HMI, and also used as a logical basis for automatically charging.
When the battery level is lower than 20%, AGV will stop receiving an assignment and go to a defined charging area for automatic charging after completing the current task. When the battery level is being replenished to equal to or higher than 20%, it will continue to receive assignments.
When the battery level is between 20% to 40%, and no assignment during a set time, AGV will also go for automatic charging. If there is an assignment during charging, AGV will stop charging and go to perform its assignment.
When the battery is fully charged, the contactor both in AGV and the charging station will break off the power circuit. The charging process is completed and AGV will wait for its next assignment.
Besides, AGV can be charged according to its assignment state, when no new assignment is dispatched after it finishes the last one, AGV will go to the charging area to charge while waiting for its assignment. It will stop charging and go to perform its assignment when the new one is dispatched.
The battery’s BMS system monitors the charging situation, when over-current, over-voltage, over-temperature, and short circuit is detected, the battery will disconnect the charging interface, so that the charging stops, at the same time, it will show a red light alarm and HMI interface alarm.
1. Smart control: The current AGV charging technology is not intelligent enough, and it doesn't work well on some types of AGV. In order to apply automatic charging in all kinds of industries, the smart control method of charging needed to be improved to reduce the risks of human interference.
2. Improve efficiency: In recent years, besides the development of online charging has increased AGV working efficiency, with more types of AGV showing up, some AGV manufacturers have launched standardization, serialization and modularization research of wireless charging, which has provided great conveniences of AGV installation and use.
3. Network data exchange: Nowadays, the AGV communication method has entered the Internet Plus era. With the help of IoT and big data technologies, more and more powered products can use the technical connections to collect power data that the Client cannot detect and send feedback, which allows precautions to be made.
4. AGV smart control system: AGVS and PMS systems can be directly connected with MES, WMS, EPR from client-side to realize data exchange between systems.

With exquisite and compact design of bumping charging station, the AGV wireless charging station with QR code robot navigation can save occupying space.
Low power value and end charging power value can be set according to demands.
When AGVs need to be charged, they will automatically move to the AGV wireless charging station for charging and continue to execute other tasks after charging is completed.
The charging area is built with a wireless power transmission device, and the AGV is installed with the wireless power receiving device. The AGV working time and charging time can be set in advance. After AGV works for a period of time it will symptomatically to the charging area, the charging area energy transmitter automatically recognizes it and starts charging.
The wireless charging system contains three closed circuits, including power supply circuit, charging circuit, and discharging circuit, of which the power supply closed circuit is composed of battery management system, lithium-ion capacitor module and regulated power supply to provide driving voltage for AGV; charging closed circuit is composed of wireless charging receiving device, charging terminal, battery management system and lithium-ion capacitor module to supplement power for the regulated power supply; discharge closed circuit is composed of regulated power supply, AGV brake plate and brake resistance, which can consume excess electrical energy.
The wireless charging system realizes the wireless fast charging of AGV through the magnetic coupling resonant energy transmission technology and the charging closed circuit. It is stable in operation, precise in positioning charging devices and safer in use since it has no sparks caused by contact charging.
The wireless charging system can be used for mobile robot wireless charging, AGV wireless charging, and AGV automatic charging, mainly suitable for AGV wireless charging system with 24V/48V motor drive, and with the maximum charging current of 20A. The transmitter and receiver of this product adopt the integrated design of power converter and coupling mechanism; the receiver is small, lightweight, and easy to install and use.
Main features
The charging process is wireless, no need for contact between contact plate and current collector a; wide charging range, no need for precise alignment; no bare contact plate, no electrode oxidation, fouling and other issues; isolated from the power grid, which will not pose a threat to personal safety; with over-current, over-voltage, over-temperature, short-circuit , FOD and other protections.
Wireless charging is a non-contact charging device, it does not require cables to connect the vehicle to the power supply system. It abandons the charging contact, and avoids the use of port to achieve a physical connection of the circuit. This avoids contact wear, arc sparks and high requirements for AGV positioning. And in some use cases that require automatic charging, there is no need for expensive electric actuators, which greatly reduces the cost. Wireless charging technology enables electrical isolation between the charging end and the AGV energy storage system. The wireless charging method is safer than in-line charging method, due to its contactless charging approach and high degree of intelligence,which has fundamentally eliminate the drawbacks caused by the in-line charging method . Moreover, it is more applicable and intelligent, since it can start charging as soon as AGV comes and stop as soon as AGV left.






(1).webp)




.webp)










.webp)