 Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
 Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
Focus on AGV industry for 18 years
In the automotive industry, production processes are fixed, and the degree of standardization is high. The application of smart logistics in the automotive sector has also become more mature, with widespread use in the main assembly lines, engine production lines, and transmission assembly lines. Smart logistics not only enables automated delivery of components but also supports flexible assembly and manufacturing.
The client for this project is a leading enterprise in automotive engine manufacturing, undertaking an expansion project for its assembly line, increasing monthly production capacity from 120,000 to 180,000 units. The project uses one-way towing mobile robots to transport material carts, improving logistics efficiency and reducing labor costs.
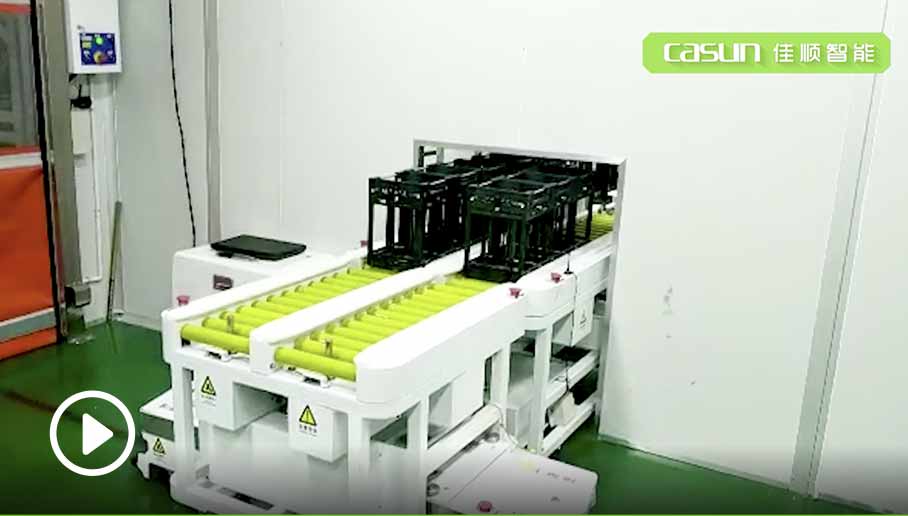

There is a wide variety of material types and frequent switching of vehicles, with each material model requiring a corresponding vehicle match to ensure accuracy. This makes scheduling more flexible and supports a diversified, flexible production model.
Through identification and detection, the exact position and orientation of each component are ensured. Real-time updates on material status are provided, ensuring the integrity of the data chain and forming a closed-loop information system.
On the complex production line in the PACK section, multiple AMRs must work in coordination to avoid collisions while maintaining an efficient production flow. This ensures real-time production demands are met, maximizing manufacturing efficiency.

The project utilizes 31 SLAM navigation rear-towing mobile robots, 8 automatic charging stations, the CRMS mobile robot intelligent control system, and a quick-rolling door docking system.
The mobile robot intelligent control system interfaces with the customer's MES system, testing system, interface platform system, and EOL (End-of-Line) testing system. The testing equipment's PLC sends commands, which are converted into tasks by the CRMS system, enabling data sharing and signal integration, thus improving transport and production efficiency.
SLAM navigation mobile robots are used to autonomously transfer material carts in a rear-towing manner, enabling material transport between the ingredient area, filling area, and mainline. These robots complete tasks such as product assembly and testing. The CRMS central control system communicates with the production line MES to achieve intelligent control of the entire line and mobile robots.
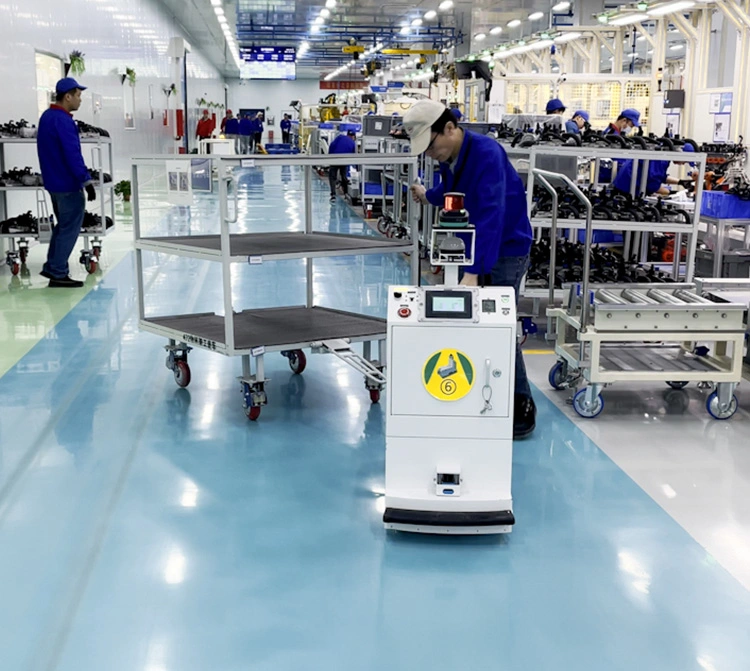


Lower the investment in fixed equipment, create a flexible production line, and improve scheduling flexibility; increase the yield rate and accuracy.
Achieve intelligent in-house logistics by optimizing warehouse locations, paths, and task assignments, and implementing full-process information management.

Accurately collect data on material efficiency, frequency, utilization, etc., and use the analysis to improve processes and enhance efficiency.
